How Does a Capacitor Work in a Fan? A fan is just one of the many electrical devices that require a capacitor as a necessary component. When it comes to the operation of the motor in a fan, the capacitor is an essential component since it supplies the necessary starting torque and regulates the fan’s speed.
The science that goes into the operation of common household equipment like fans can be better appreciated if we have a better understanding of how capacitors work.
In this post, we will explore the fundamentals of capacitors, as well as the different types of capacitors and the unique role that each type plays in fan motors.
In addition, we will investigate how capacitors contribute to the overall energy efficiency of these cooling devices as well as how they ensure a smooth operation of the fans.
I. What is a Capacitor?

A component of an electrical circuit that can both store and release electrical energy is called a capacitor. It is made up of two conductive plates that are separated by a dielectric, which is a type of substance that provides insulation.
The application of a voltage between the plates causes electrons to gather on one of the plates, resulting in the formation of a negative charge, while the other plate becomes positively charged.
This separation of charges between the plates results in the creation of an electric field between the plates, and the capacitor uses this field to store electrical energy.
The amount of charge that can be stored in a capacitor is determined by its capacitance, which is measured in farads and can be found in capacitors of many shapes and sizes.
Electronic circuits make extensive use of them to eliminate voltage swings, filter out noise, and provide oscillators with timing elements.
In addition, capacitors play an important part in motor applications, such as fans and compressors, where they assist in starting the motor and regulate the speed of the motor while it is operating. Capacitors also play an important role in electrical storage.
II. Types of Capacitors:

Capacitors come in a variety of forms, each of which is optimized for a distinct class of applications by virtue of characteristics including capacitance, voltage ratings, temperature tolerance, and frequency responsiveness, amongst others.
The following is a list of some typical types of capacitors that are used in fan motors and other types of electronic devices:
- Ceramic capacitors are quite popular in high-frequency applications because of their low cost and small size. Ceramic is utilized as the dielectric material in these capacitors, and the capacitors themselves are made of ceramic.
- Electrolytic Capacitors Electrolytic capacitors have a larger capacitance than other types of capacitors and are frequently employed in circuits that supply power. Aluminum and tantalum are the two metals that can be used to create them.
- Film capacitors are utilized in a broad variety of applications due to the fact that they have high capacitance values and are reliable. Film capacitors employ a thin plastic film as the dielectric material and are constructed with this material.
- Polystyrene Capacitors: These capacitors have great temperature stability and low dielectric loss, making them useful for precise applications because of their combination of these two characteristics.
- Capacitors with a Variable Capacitance: As the name says, these capacitors have a capacitance that can be altered to control the frequency in radio and tuning circuits. As the name suggests, these capacitors have a variable capacitance.
- Motor Run Capacitors: Motor run capacitors are designed to continually work while the motor is running in order to improve the motor’s efficiency and power factor. These capacitors are specifically utilized in fan motors, but they are also used in other types of motors.
Because every type of capacitor has a unique combination of benefits and drawbacks, it is vital to select the appropriate type of capacitor in accordance with the particular specifications of the electronic fan or device that it will be used in.
III. How Capacitors Work in Fan Motors:

Capacitors are an essential component in the starting and continued operation of the motors found in fan systems. The start capacitor and the run capacitor are the two kind of capacitors that are utilized most frequently in fan motors.
Start Capacitor: When you turn on the fan, an electrical charge is momentarily stored in the start capacitor for a short time. After that, the charge is transferred to the auxiliary winding of the motor, which results in the formation of a spinning magnetic field.
This field supplies the initial torque that is required to overcome the inertia of the fan blades and begin turning the motor’s crankshaft.
Run Capacitor: After the start capacitor has been removed from the circuit and the motor has begun to rotate, the run capacitor will now be responsible for holding the charge.
The run capacitor will continue to provide a phase shift to the secondary winding of the motor, which will ensure that the operation is both smooth and effective.
When used in fan motors, capacitors allow for increased energy economy as well as higher torque during the starting phase of operation.
Capacitors allow for a speedy and trouble-free beginning to the motor’s operation by supplying the phase shift that is necessary to generate a revolving magnetic field.
It is absolutely necessary to select the appropriate capacitors for fan motors, as the utilization of capacitors with wrong values might result in faults of the motor in addition to a decrease in performance.
The effective operation of fan motors may be ensured by performing routine maintenance and replacing capacitors on a regular basis. This can also assist increase the lifespan of the motors.
IV. Capacitor-Start Fan Motors:
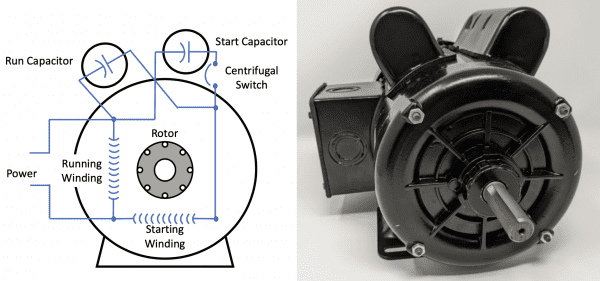
A form of single-phase induction motor known as a capacitor-start fan motor is typically found in ceiling fans, exhaust fans, and various other types of small appliances.
These motors come equipped with both a start capacitor and a run capacitor, which allows for a significant amount of starting torque in addition to an effective running operation.
When the switch for the fan is turned on, the start capacitor provides a momentary boost in torque to get the spinning started.
The start capacitor is detached once the fan achieves its operational speed, and the run capacitor takes over to continue the performance of the motor once it has been activated.
Because of their design, capacitor-start fan motors can be cost-effective, efficient in their use of energy, and suited for a wide range of applications requiring fans.
V. Capacitor-Run Fan Motors:

One further form of single-phase induction motor that is frequently used in fans and other types of tiny appliances is the capacitor-run fan motor.
In contrast to motors that start using a capacitor, those that run using a capacitor only require a single capacitor, which is responsible for both starting and operating the motor.
This capacitor is linked to the motor at all times, including while it is starting and running; as a result, it delivers a greater torque when the motor is first turned on and improves its efficiency when it is operating.
Because they are dependable, require less in the way of upkeep, and have a higher power factor, motors that are operated by capacitors are, in comparison to other types of motors, more energy efficient.
In fan motors that are powered by capacitors, the capacitor generates a phase difference between the main and auxiliary windings, which results in the production of a spinning magnetic field that sets in motion the fan.
The capacitor continues to provide the necessary phase shift even after the motor achieves its operating speed, ensuring that the operation is as smooth and effective as possible.
Because of their low price and great performance, these motors find widespread application in a variety of fan applications including ceiling fans, air circulators, and other fan applications.
VI. Energy Efficiency and Power Factor Correction:

Fan motors that are powered by capacitors are renowned for their energy efficiency and power factor correction. The power factor quantifies the efficiency with which electrical power is utilized in a circuit.
A power factor of 1 indicates that all available power is being utilized effectively, whereas a power factor of less than 1 indicates that some power is being wasted.
In capacitor-operated motors, the capacitor improves the phase relationship between the motor’s voltage and current to rectify the power factor. This means that the motor consumes less reactive power from the electrical supply, which decreases waste and increases overall efficiency.
In addition to reducing energy consumption, a higher power factor also benefits the electrical system. It helps reduce transmission losses, voltage drop, and transformer and other electrical equipment duress.
Numerous nations have regulations and incentives to promote the utilization of energy-efficient motors with enhanced power factor.
In addition to power factor correction, capacitor-run fan motors are intrinsically more efficient than other motor varieties due to their design and use of capacitors.
They are an attractive option for a variety of fan applications due to their increased efficiency, which reduces energy consumption and electricity expenditures.
Capacitor-driven fan motors are not only dependable and cost-effective, but they also contribute to energy conservation and a greener environment by fostering increased energy efficiency and power factor correction in electrical systems.
VII. Common Capacitor-Related Issues in Fans:

Over time, capacitors in fan motors may degrade or fail due to factors such as temperature fluctuations or voltage spikes.
Common issues include reduced starting torque, irregular fan speed, and motor overheating. Identifying and replacing faulty capacitors is essential to ensure the fan’s optimal performance and longevity.
FAQ Related to How Does a Capacitor Work in a Fan
What is the function of a capacitor in a fan motor?
What are the types of capacitors used in fan motors?
How do capacitor-start fan motors work?
What are capacitor-run fan motors?
How do capacitors contribute to energy efficiency in fans?
What are common issues related to capacitors in fans?
How can users ensure their fans work efficiently for a long time?
Are all fan motors equipped with capacitors?
Can a faulty capacitor be replaced, or is it better to replace the entire fan?
Are capacitors used only in electric fans, or are they found in other appliances as well?
Conclusion:
In conclusion, capacitors are indispensable components in fan motors, providing the starting torque and regulating speed. Their role in enhancing energy efficiency and power factor correction makes them vital in modern fan designs, ensuring smooth operation and lower energy consumption for users.
- Are BLDC Fans Reliable? Exploring the Advantages and Reliability of BLDC Ceiling Fans
- Understanding the Differences Between Axial Fans and Centrifugal Fans
- Demystifying Fan Technology: How Does a Capacitor Work in a Fan?
- Top 7 Best Ceiling Fans in India 2023 with price and buying Guide
- Hello world!
- 5 best ceiling fan under 1000 Rs In India 2022 >> Price, Review, Specifications
Comments
Post a Comment